If you feel severe and continuous pain, swelling, and a bad taste in your mouth, it can be due to an infected tooth. Sometimes, it’s necessary to remove an infected tooth to alleviate pain and stop the spread of infection to nearby areas. Infected tooth extraction is a common dental procedure that is considered when all other methods to save the tooth, like antibiotics or root canal therapy, are no longer applicable or have failed.
Some common dental infection symptoms are:
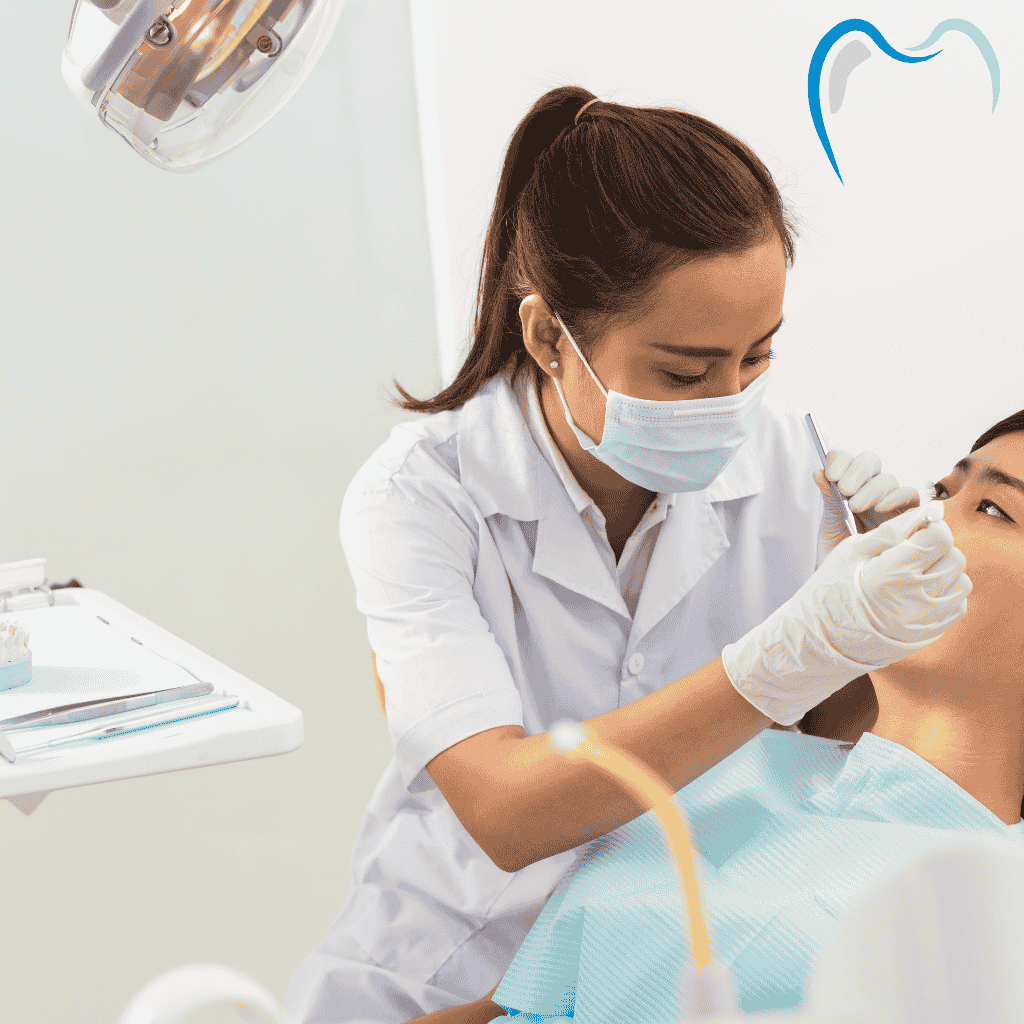
There is a common believe that if a tooth is infected or abscessed, it should not be removed until the infection has cleared up. However, in most cases pulling an infected tooth is the best way to clear the infection. The method of treatment depends on where the infection is and how serious it is.
Extract a tooth that is infected when:

Following the extraction of an infected tooth, treatment typically involves clearing the affected area to remove debris, pus, or bacteria. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed to treat the infection effectively. It’s important to complete all your antibiotic courses, even if the symptoms are improved, to fully eradicate the bacteria.Rinsing with warm saline water will aid in healing. Additionally, avoid smoking and alcohol because they slow down the healing process.
Tooth extractions have become quite a safe and routine dental procedure with modern dental techniques,but like any other surgery, infected tooth extraction also come with some potential risks and complications.
Most common problems after infected tooth extraction are :
Its normal to have some localised pain and swelling during the first 24 to 48 hours following tooth extraction which gradually subsides as healing progresses.Using Ice packs can help to reduce the swelling and tooth extraction pain.
The other most common complication with infected tooth extraction is a Dry socket . It is the most painful condition that occurs after tooth extraction. When a tooth is removed, a blood clot is formed in the socket to protect the underlying nerves and bone. If this clot is dislodged or fails to create, it can expose the underlying bone and nerves to air, food, and bacteria in the oral cavity, causing intense pain and a bad taste in the mouth. It can also slow down the healing process much more than expected.
An abscessed tooth is infected, and manipulating the tooth during an extraction can potentially cause the infection to spread to surrounding tissues, bones, or into the bloodstream. This can lead to more severe health issues, including potentially life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
Nerve damage is another dental extraction complication that occurs most commonly in the lower jaw because lower teeth are close to the inferior alveolar nerve. Nerve damage can cause numbness or pins and needles-like sensations in the chin, lip, and tongue area. If nerve damage occurs, your Dentist may monitor the situation closely. In rare cases, surgery may be required.
The upper molars are close to the sinus cavity. While extracting upper molars, there is a small risk of perforation into the maxillary sinus. This is most common when the roots are decayed or deeply embedded. Treatment includes closing the hole and additional medications.
Infected Tooth extraction is generally a safe and effective procedure for dealing with dental problems, but like all other surgeries, there is a risk of complications. With knowledge and guidance, you can reduce the risk of dental complications by following the aftercare instructions properly. Always reach out to your Dentist if you face any issues for timely treatment and guidance.
Disclaimer: Health content shared on this website is for educational and informational purpose only not a substitute for professional medical advice,diagnosis and treatment.
All rights reserved @ healthblogger.online